Evaluating the accuracy of the multi-pool tissue parameters is challenging due to the lack of a gold standard for validation. To establish rigorous validation of the saturation transfer (ST) MRF method, synthetic MRI analysis was performed by solving inverse (e.g., ST-MRF reconstruction) and forward Bloch-McConnell equations, as shown in the figure.1 Initially, in vivo tissue parameters maps were estimated from the ST-MRF reconstruction using 103 dynamic images acquired with a pseudorandomized schedule (MRF schedule A). Subsequently, new ST-MRF images were synthesized using these tissue estimates and new MRF schedules (MRF schedule B) via Bloch-McConnell equations and were compared with true image acquisitions. The synthesized ST-MRF images exhibited a high degree of agreement with the ST-MRF images obtained from the MRF schedule B (RMSE = 3.2%). The estimated tissue parameters were deemed satisfactory under the different scan parameter conditions of the new MRF schedules. The second figure presents the standard images and tissue parameter maps from ST-MRF reconstruction (Recon-FCNN) in a brain tumor patient with an infiltrating glial tumor. The saturation transfer MRF improves the accuracy and reliability of the protein concentration and pH measurements in a clinically feasible scan time, on a 3T scanner with high image quality.
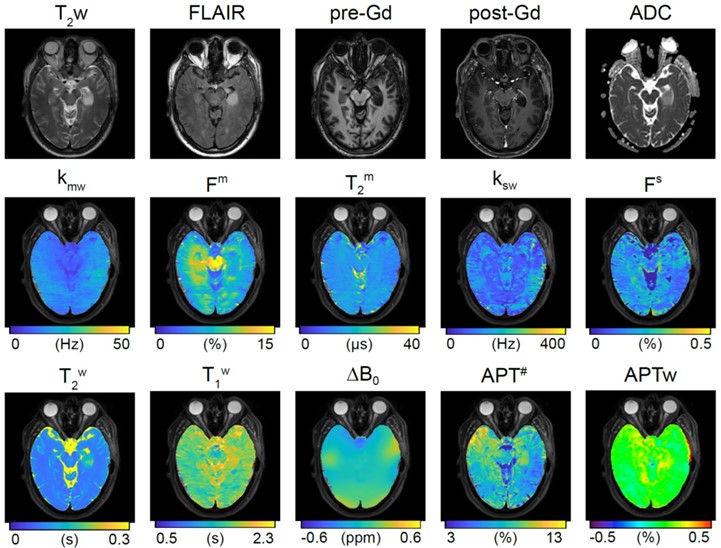
Figure: Top row. Clinical images. Bottom rows: MRF results in quantitative images of multiple parameters, including relaxation times (T1, T2) for tissue water (w), proton exchange rates between tissue compounds (m = semisolid, s = solute) and water, and tissue component fractions F. Field variation maps (delta-B0) and amide proton transfer (APT) maps can also be generated.
- M. Singh, B. Kang, SZ Mahmud, P.C.M. van Zijl, J. Zhou, and H-Y. Heo, Saturation transfer MR fingerprinting for magnetization transfer contrast and chemical exchange saturation transfer quantification. Magn Reson Med. 2025 Apr 14;94(3):993–1009.
